
get(int row).remove(int index) : It helps in deleting an element present at a particular index of ArrayList in a given row. remove(int row) : It helps in removing a particular row from our ArrayList.

get(int index).indexOf(Object element): It helps in finding the index of particular element in our ArrayList in a particular row. get(int index) : It helps in getting the index of the ArrayList where the required element is to be added. add(int index, Object element) : It helps in adding the element at a particular index. add(Object element) : It helps in adding a new row in our existing 2D arraylist where element is the element to be added of datatype of which ArrayList created. Java 2D ArrayLists has various methods such as The following are diiferent ways to initialize a 2D ArrayList: import
We just need to import it using - import It is a generic class already defined in java. When it is filled completely, the size increases automatically to store the next element. Here also, we do not need to predefine the size of rows and columns.

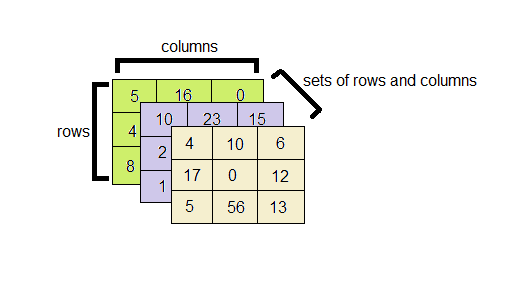
2-D Array ListĪ two dimensional array list can be seen as an array list of an array list. In this article, we'll dive deeper into it, studying about its implementation, advantages and disadvantages. The most common and the simplest form of Multidimensional Array Lists used is 2-D Array Lists. In Java we have Collection framework which provides functionality to store multidimensional Array List which is commonly called Multidimensional Collections (or Nested Collections) Hence, here we can store any number of elements in a group whenever we want. It is a collection of group of objects where each group can have any number of objects stored dynamically.
Now, we can add colors to points in space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
